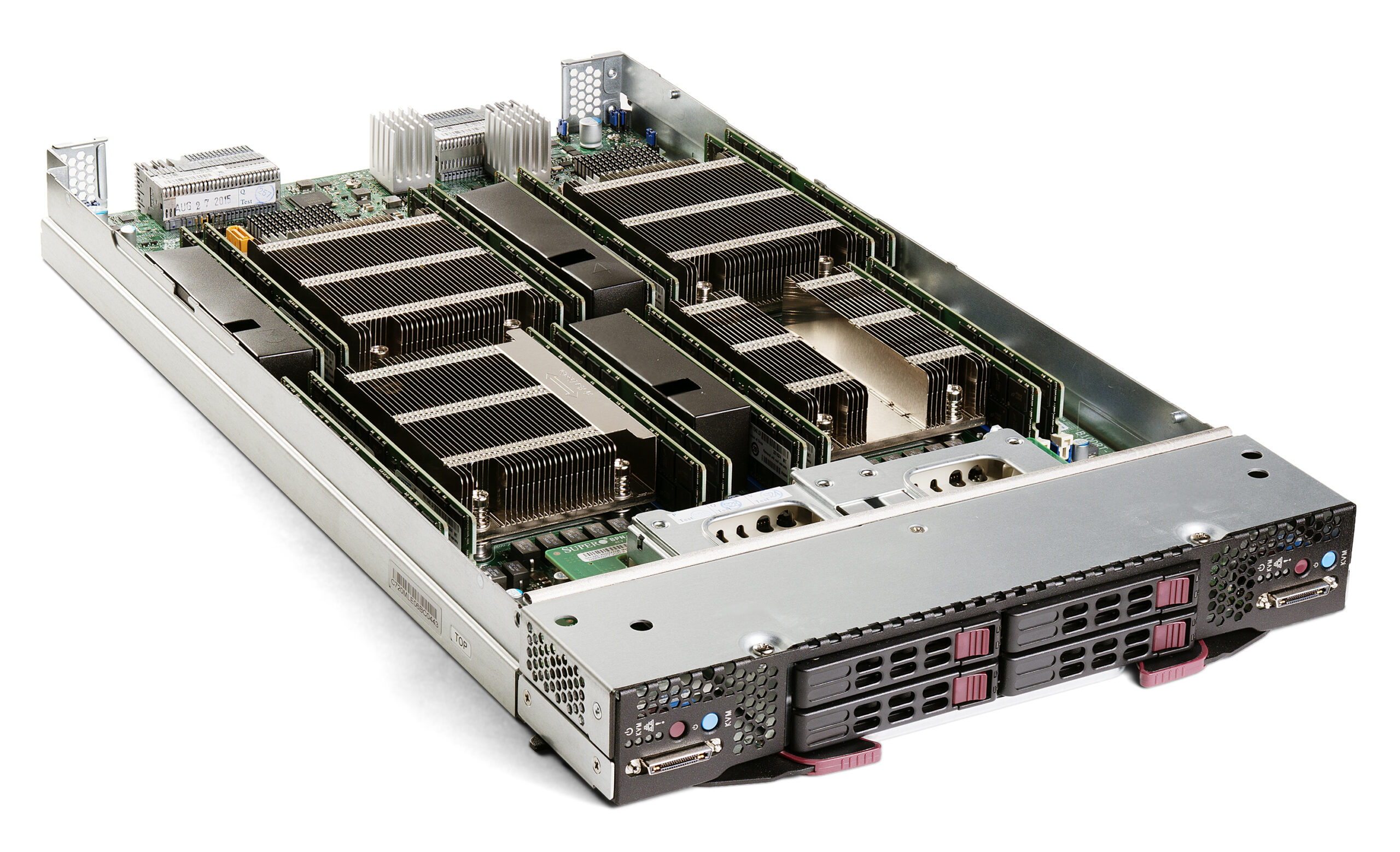
Introduction
The rapid evolution of information technology (IT) has been marked by transformative innovations that redefine the efficiency and capabilities of data center infrastructures. Among these advancements, the Blade Server Transformation stands out as a pivotal paradigm shift, revolutionizing the way servers are conceptualized, deployed, and managed within IT environments. This technological leap goes beyond mere hardware upgrades, offering a comprehensive reimagining of server architecture with a focus on high density, scalability, streamlined management, and cost-effectiveness. In this exploration, we delve into the multifaceted impact of the Blade Server Transformation, examining its key features, benefits, and the profound influence it exerts on the landscape of modern IT. As organizations navigate the complexities of ever-expanding data requirements, the blade server’s role in reshaping IT infrastructure emerges as a critical narrative in the ongoing story of technological innovation.
Revolutionizing IT: The Blade Server Transformation
Blade servers have been a transformative technology in the field of Information Technology (IT), revolutionizing the way data centers are designed, deployed, and managed. Blade server technology represents a significant advancement in server architecture, offering numerous benefits that contribute to increased efficiency, scalability, and overall cost-effectiveness.
Virtualization Integration:
Blade servers are well-suited for virtualization, a technology that allows multiple virtual servers to run on a single physical server. The high-density nature of blade server chassis complements virtualization efforts, enabling organizations to host numerous virtual machines within a compact space. This consolidation of resources enhances resource utilization and flexibility, as virtual servers can be dynamically provisioned or scaled based on demand.
Flexibility in Blade Types:
Blade server chassis supports various types of blades, each optimized for specific functions such as computing, storage, or networking. This flexibility allows organizations to tailor their infrastructure to meet specific workload requirements. For example, compute-focused blades might include powerful processors and memory, while storage blades can be configured with ample disk space.
Converged Infrastructure:
Blade servers contribute to the concept of converged infrastructure, where compute, storage, and networking components are tightly integrated into a single platform. This convergence simplifies the deployment and management of data center resources, as administrators can work with a unified system rather than dealing with disparate components. Converged infrastructure solutions often include pre-configured and validated setups, accelerating deployment times.
Adoption of Advanced Networking Technologies:
Blade servers often feature advanced networking technologies, such as high-speed interconnects like InfiniBand or 10/25/40/100 Gigabit Ethernet. This allows for faster data transfer within the data center and supports the increasing demands of modern applications and workloads. Advanced networking capabilities contribute to improved performance and responsiveness of the overall infrastructure.
Remote Management and Automation:
Blade servers come equipped with remote management interfaces, often based on technologies like Intelligent Platform Management Interface (IPMI) or out-of-band management. These interfaces enable administrators to remotely monitor and control servers, even if the operating system is unresponsive. Automation features further enhance efficiency by allowing tasks such as provisioning, configuration changes, and updates to be performe programmatically.
Security Enhancements:
The centralized nature of blade server management facilitates more robust security practices. Security policies, updates, and access controls can be uniformly applied across all blades within a chassis. Additionally, physical security is often improved, as blade servers are house in a locked. Monitored chassis, reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
Interoperability and Standards:
Blade servers adhere to industry standards, promoting interoperability between different vendors’ hardware and software components. This adherence to standards enhances flexibility and avoids vendor lock-in. Allowing organizations to select the best-of-breed components for their specific needs.
Environmental Considerations:
The efficiency gains from blade servers contribute to environmental sustainability. By reducing the physical footprint, optimizing power usage, and improving cooling efficiency, organizations can minimize their impact on the environment. This aligns with the growing emphasis on green IT practices and corporate social responsibility.
Evolving Blade Server Technologies:
The blade server landscape continues to evolve with advancements in technology. New generations of blades often feature more powerful processors, increased memory capacities, and improved energy efficiency. Staying abreast of these advancements enables organizations to continually optimize their infrastructure for performance, reliability, and cost-effectiveness.
Unlocking Performance: The Blade Server Revolution
The blade server revolution represents a significant advancement in data center architecture. Offering a more efficient and scalable solution compared to traditional rack-mounted servers. Blade servers are design to optimize space, power, and cooling while providing high-performance computing capabilities.
Compact Design:
Blade servers are more compact compare to traditional servers, allowing for higher density within a smaller footprint. Multiple blade servers can be house in a single chassis, sharing common resources like power supplies and cooling systems.
The reduced physical space requirements enable data centers to maximize their floor space. Accommodate more computing power, contributing to increased overall efficiency.
Scalability:
Blade servers are design for scalability, making it easier to expand computational resources as needed. IT administrators can add or remove blade servers from a chassis without disrupting the entire system, providing a flexible and scalable infrastructure.
This scalability is crucial for businesses experiencing growth or fluctuations in computational demands, allowing them to adapt their infrastructure accordingly.
Modular Architecture:
Blade servers follow a modular architecture where individual blades function as self-contained server units. Each blade typically includes its own processors, memory, storage, and network interfaces.
This modular approach simplifies maintenance and upgrades. Administrators can easily swap out or upgrade individual blade components without affecting the entire system. Minimizing downtime and streamlining hardware management.
Resource Efficiency:
Blade servers share common resources, such as power supplies and cooling systems, which improves overall energy efficiency. This shared infrastructure reduces the amount of redundant components, leading to lower power consumption and operational costs.
The efficiency gains contribute to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly data center operation.
Centralized Management:
Blade server systems often come with centralized management tools. That allows administrators to monitor and control the entire infrastructure from a single interface. This centralized management simplifies day-to-day operations, enhances visibility, and streamlines the configuration of resources.
Remote management capabilities enable administrators to address issues, perform updates, and make configuration changes without physically accessing each server.
High-Performance Computing:
Blade servers are design to deliver high-performance computing capabilities. Making them suitable for demanding workloads such as virtualization, cloud computing, and complex data analytics.
With advancements in processor technology, memory capacity, and high-speed interconnects. Blade servers can meet the performance requirements of modern applications and workloads.
Redundancy and Reliability:
Blade server systems often incorporate built-in redundancy for critical components, such as power supplies and networking. This redundancy enhances system reliability by reducing the risk of hardware failures causing service interruptions.
The hot-swappable nature of blade components allows for seamless replacement of failed components without disrupting the overall system operation.
In summary, the blade server revolution has transformed data center infrastructure by providing a compact, scalable, and efficient solution for high-performance computing. As technology continues to advance, blade servers are likely to play a key role in meeting the evolving demands of modern IT environments.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Blade Server Transformation has emerged as a cornerstone in the ongoing evolution of information technology. Leaving an indelible mark on the landscape of IT infrastructure. Through a blend of high-density design, scalability, and streamlined management. Blade servers have revolutionized the way organizations approach data center architectures. The journey from traditional server setups to the compact, modular. The efficient world of blade servers has brought forth a paradigm shift, addressing the demands of modern computing with unprecedented efficiency. The hot-swappable nature of blade components allows for seamless replacement of failed components without disrupting the overall system operation.
The impact extends beyond mere hardware upgrades; it encompasses a holistic approach to IT management, integrating virtualization, advanced networking, and converged infrastructure. The transformative power of blade servers is evident in their ability to enhance not only operational efficiency. But also to contribute significantly to cost savings, energy efficiency, and environmental sustainability. Blade server systems often incorporate built-in redundancy for critical components, such as power supplies and networking.